Prana Announces Successful Phase 2 Results in Huntington Disease Trial
Prana Announces Successful Phase 2 Results in Huntington Disease Trial
FEBRUARY 2014: MELBOURNE, Australia and NEW YORK, USA: Prana Biotechnology (ASX:PBT / NASDAQ:PRAN) has today announced the results of its Reach2HD Phase 2 clinical trial investigating PBT2 as a treatment for Huntington disease. The double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted by the Huntington Study Group at research sites in the United States and Australia. The study enrolled 109 individuals with Huntington disease who were randomly assigned to receive daily doses of either PBT2 250mg, PBT2 100mg, or placebo for 26 weeks.
Key Points:
- Primary endpoints of safety and tolerability met.
- Secondary endpoint: Statistically significant improvement in a measure of executive function (cognition) in research participants administered 250mg PBT2 daily (p=0.042).
- PBT2 250mg was also associated with a favourable signal in functional capacity.
- Preliminary evidence suggests PBT2 250mg reduced atrophy of brain tissue in areas affected in Huntington disease, seen in a pilot imaging sub-study.
- Company plans to advance PBT2 to a confirmatory Phase 3 clinical trial.
Primary Objective: Safety and Tolerability
The primary endpoint of the study was met. In this study, PBT2 was safe and well tolerated. 95% (104 of 109) of participants completed the study on their assigned dose.
An independent Data Safety Monitoring Board met on five occasions over the course of the trial and on each occasion recommended that the trial continue as per the original protocol.
There were no substantial differences in adverse events across the two PBT2 dose groups and the placebo group. Only one of the ten reported serious adverse events was deemed by the clinical site investigator to be related to drug treatment. This occurred during the 4-week follow-up period (i.e. not on study drug) after completing the six month treatment.
Secondary Objective: Efficacy
The effects of PBT2 were tested on cognition, motor performance, behaviour and functional capacity, of which cognition was pre-specified as the main efficacy outcome.
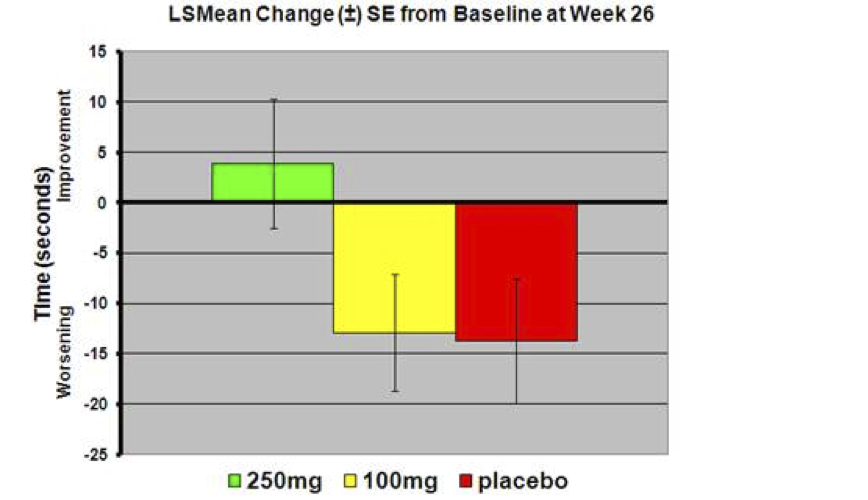
There was a statistically significant improvement in performance on the Trail Making Test Part B (as illustrated in the graph), in the PBT2 250mg group compared to placebo at both 12 (p<0.001) and 26 weeks (p=0.042).
Trail Making Test Part B is a measure of executive function (e.g., ability to plan activities), which is impaired early in the course of Huntington disease and is also affected in Alzheimer’s disease.
Given the evidence from an earlier trial that showed that PBT2 improved executive function in Alzheimer’s disease patients, the Reach2HD trial included a plan to assess the effects of PBT2 on an Executive Function Composite z-score that included the Trail Making Test Part B. There was a statistically significant improvement in this z-score (p=0.038) in a pre-specified analysis of Reach2HD participants with early stage Huntington disease, as measured by their Total Functioning Capacity score. Across all participants, which comprised both early and mid-stage patients, there was a trend to improvement (p=0.069).
Dr Rudy Tanzi, Professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School and Prana’s Chief Scientific Advisor, commented that “the observation of significant improvement in executive function with PBT2 in this clinical trial for Huntington disease and the previously reported Alzheimer’s trial, suggests a common mechanism for neurodegeneration in these diseases based on metal interactions. In my opinion, these findings significantly elevate the potential for PBT2 as an effective therapy for both Huntington disease and Alzheimer’s disease."
The improvement in executive function was accompanied by a small but favourable signal in a key measure of functional capacity. No significant improvements were seen on other secondary efficacy measures in the study.
Dr Ira Shoulson, Professor of Neurology at Georgetown University and Chair of the Huntington Study Group, who was not involved in the trial and acts as an advisor to Prana, added: “In the Reach2HD trial, the improvement in executive function performance was also accompanied by a favourable signal of a slowing of functional decline, as measured by the Total Functional Capacity score. This is the first time we have observed dose-related slowing in functional decline over a six month period of treatment – which taken together with the safety reassurance – will provide genuine optimism for the Huntington disease community to support a larger confirmatory trial of PBT2 in Huntington disease.”
Exploratory Finding
As Huntington disease and other neurodegenerative disorders progress, there is a gradual loss of brain tissue or atrophy. In Reach2HD, brain imaging using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed in a small subset of patients (n=6) to map anatomical changes in brain structure. In the combined PBT2 groups (n=4) a reduction in atrophy of brain tissue in regions of the brain known to be affected by Huntington disease was observed compared to the placebo group.
Dr Diana Rosas, Associate Professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School and the study’s co-Principal Investigator who conducted the imaging sub-study commented: “Despite the very small number of patients in the sub-study, the data are suggestive of a beneficial effect of PBT2 in regions of the brain that are known to be vulnerable to Huntington disease.”
Dr Ray Dorsey, Professor of Neurology at the University of Rochester and the Principal Investigator on the trial added: “We are very pleased that the results of the Reach2HD study have shown that PBT2 is well tolerated and generally safe over six months in individuals with early to mid-stage Huntington disease.”
“In addition, the results indicated a significant benefit on cognition that is consistent with the previous trial in Alzheimer’s disease and is accompanied by an encouraging finding in functional capacity. We are very thankful for the involvement of the research participants and investigators in this study and look forward to future trials of this promising therapy for one of the cardinal features of Huntington disease.”
Prana plans to advance PBT2 into a confirmatory Phase 3 clinical trial that could allow PBT2 to be approved for the treatment of Huntington disease.
A clinical appendix accompanies this announcement.
For further information please visit the Company’s web site at alterity-therapeutics.adrianbeyerle.com.
For patient enquiries please contact [email protected] or call 1300 13 90 33.
Contacts:
Global Investor Relations Lead Investor Relations (USA)
Rebecca Wilson Josh Drumm
T: +61 3 8866 1216 T: +1 (347) 327-2863
E: [email protected] E: [email protected]
Media Relations (Australia) Media Relations (US)
Ben Oliver Jason Rando
T: +61 3 8866 1233 T: +1 (347) 327-2863
E: [email protected] E: [email protected]
Clinical Appendix
PBT2-203 “Reach2HD” Study Design and Results
|
Number of patients |
109 patients randomized; 104 patients completed study. |
|
Key patient selection criteria |
§ Men and women with clinical features of Huntington disease (HD) and a CAG repeat number ≥ 36 |
|
Rationale |
PBT2 is a moderate affinity metal ligand that inhibits metal mediated toxic gain of function of disease proteins such as mutant Huntingtin. In addition, the ionophore capability of PBT2 facilitates the redistribution of copper and zinc to their correct brain tissue compartments. Collectively, PBT2 has been shown to reduce toxic protein accumulation, support synaptic plasticity and promote neuronal growth and function in animal models. |
|
Blinding |
Double-blind |
|
Placebo controlled |
Yes |
|
Route of administration |
Oral (capsules) |
|
Study design |
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel three-group study to assess the safety and tolerability, and efficacy of PBT2 in patients with early- to mid-stage HD. An independent Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) provided patient safety monitoring at regular intervals throughout the study. |
|
Dose groups |
0mg (placebo capsules of identical appearance), 100mg and 250mg |
|
Duration |
34 weeks: Four week Screening period, 6 month (26 week) treatment period and Follow-up 4 weeks post treatment. |
|
Primary Objective: Safety and Tolerability |
Endpoints: |
|
Secondary Objectives: Efficacy |
Endpoints:
Category Fluency Test, Trail Making Test Parts A and B, Map Search, Symbol Digit Modalities Test, Stroop Word Reading Test, Speeded Tapping Task, MoCA.
Urine: 8 hydroxy 2'deoxyguanosine; creatinine |
|
Exploratory Sub Study |
Brain Volumes and Function: MRI |
|
Trial sites |
20 clinical trial sites across USA (15) and Australia (5) |
|
Efficacy Analysis populations |
All efficacy analyses were conducted on the Intention-to-Treat (ITT) population. Efficacy analysis on the Per Protocol (PP) population was to be performed if the PP population comprised more than 95% or less than 50% of the ITT population. |
|
Patient Demographics |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Primary Objective: Safety and Tolerability |
PBT2, in this study of early- to mid-stage HD patients, was safe and well tolerated, with no significant findings or trends in any of the safety parameters measured. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Secondary Objectives: Efficacy |
Main Composite Cognition z-score and Exploratory Composite Cognition z-score. No statistically significant changes. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Secondary Objective: Efficacy |
No significant changes were seen in motor, functional, behavioural or global assessments in either PBT2 treatment group compared to placebo over the 26 week treatment period. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Secondary Objective: Efficacy–Biomarker Endpoint |
There were no significant changes in the urine or blood biomarkers assessed at week 26 with PBT2 treatment compared to placebo. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Secondary Objective: |
Changes in cortical thickness (mm) were mapped at week 26 for the combined treatment group (n=2 250mg and n=2 100mg) compared to placebo (n=2). The rate of thinning in the placebo group was faster than in the treated groups; however the effects did not reach statistical significance. |